Wed Jun 23 2021 · 5 min read
How the Crisis Affected Armenia's Telecommunications Sector

By Suren Parsyan
Illustration by Armine Shahbazyan.
The rapid growth of the world economy in recent decades is due to innovations in the field of information and high-technology, and their impact on all other fields.
The telecommunications sector in the Republic of Armenia also has an important role in economic development and growth; fast reliable connections are a prerequisite for areas like IT and banking, among others. It is the cornerstone of the most productive elements of Armenia’s economy.
It should be noted that, in 2020, Armenia's telecommunications sector accounted for 3.7% of GDP. Armenian companies introduced 4G technology for wireless communications back in 2011, the first among CIS countries and, at the time of its introduction, the 10th in the world.
The sphere of the telecommunication and communication services of Armenia consists of four main components:
• Wired telecommunication system services;
• Wireless telecommunication system services;
• Satellite communication services;
• Other types of telecommunication services.
The first sub-sector includes fixed telephone communication and broadband Internet services with fixed modems, telegraph communication and cable TV services. The second sub-sector covers mobile telephone communication, microwave radio relay, mobile broadband Internet access and other wireless (non-satellite) telecommunication services. The third is satellite services (including telephone communications, television and Internet access), and the fourth is telecommunications and communication services, which are not included in the activities listed in the previous three types.
It should be noted that, among these directions, the main ones developed in Armenia are services providing fixed and mobile telecommunications, and Internet connection via fixed and mobile modems and mobile phones.
Also of interest is the structure of revenue from telecommunications, which is presented in the following chart. As of June 23, 2021, 512 AMD is equivalent to 1 USD.
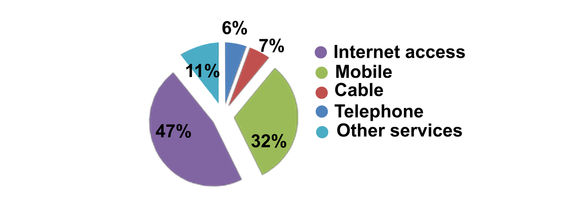
Revenue from telecommunications in 2020 amounted to 126.5 billion AMD, (4.5% less than the previous year) of which telephone (wired) constituted 7.1 billion AMD (12.2% decrease) telegraph - 5 million AMD (41.9% decrease); maintenance and operations of cable TV systems - 6.8 billion AMD (1.3% increase), mobile - 40.0 billion AMD (23.7% decrease); Internet access - 58.7 billion AMD (10.6% increase); satellite - 33.7 million AMD (30.6% increase) and other services - 13.7 billion AMD (13.9% increase).
Revenue from telecommunications in January-March 2021 amounted to 30.9 billion AMD, which has increased by 0.3% compared to the same period of the previous year. Telephone (wired) constituted 1.6 billion AMD (9.2% decrease); telegraph - 1.6 million AMD (6.7% increase); maintenance and operations of cable TV systems - 1.8 billion AMD (8.7% increase); mobile - 9.5 billion AMD (3.5% decrease); Internet access - 14.9 billion AMD (4.4% increase); satellite - 10.3 million AMD (7.3% increase) and other services - 2.9 billion AMD.
There are about 36 companies operating in the telecommunications sector of the Republic of Armenia, the main services of which include the provision of mobile and fixed communication services, cable and wireless Internet, and IT infrastructure services. It is noteworthy that, on the whole, the telecommunications companies provide their services mainly to the domestic market, and not for export. In addition, it should be noted that the revenues from mobile services command a larger share of revenues in the telecommunications sector of Armenia.
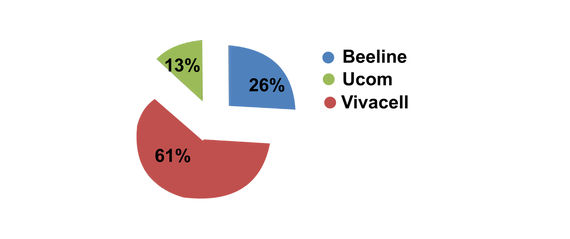
Currently, there are three mobile operators in the Republic of Armenia; in particular, Veon Armenia (which operates the Beeline brand, a member of the VimpelCom group of companies), VivaCell/MTS (a subsidiary of the Russian MTS company) and Ucom.
In 2020, the number of subscribers for Internet access in Armenia was 3,087,300, an increase of 0.2% compared to the previous year. At the same time, the number of mobile subscribers was 3,493,000, decreasing by 5.6% compared to the previous year. In general, the slowdown in the growth of telecommunications indicates the saturation of the market.
If we refer to the indicators characterizing the large economic entities operating in the telecommunications and communication sectors, we have the following image:
According to 2020 fourth quarter data, VivaCell/MTS has 2,146,888 active subscriber numbers, of which 1,900,390 are prepaid subscribers and 246,498 are postpaid subscribers. The number of broadband Internet subscribers is 53,675, new activations are at 146,687 and the attrition rate (rate at which subscribers leave) is 106,071.
In the same timeframe, the number of active subscriber numbers for Veon (Beeline) Armenia is 904,689, of which 784,133 are prepaid subscribers and 120,556 are postpaid subscribers. The number of broadband Internet subscribers is 55,531, new activations are 64,378, and the attrition of subscribers is 66,958.
Ucom’s active subscribers are at 441,399, 296,965 of which are prepaid subscribers and 144,434 are postpaid subscribers. The number of broadband Internet subscribers is 153,203, new activations are 46,062, and the attrition of subscribers is 32,628.
It should be noted that the next largest company operating in this sphere is GNC-Alfa CJSC (Rostelecom), which has 58,493 subscribers using Internet services.
Armenia’s telecommunications sector has a significant impact on the labor market as well. In particular, in 2020, the number of employees in the Information and Communication sector was 26,711, of which 1,749 were civil servants and 24,961 were in the private sector. The number of employees increased by 11.8% during the period under review. In particular, the number of employees in the private sector increased by 13.1%, while the number of employees in the public sector decreased by 5.6%.
As early as March 2021, the number of employees in the Information and Communication sector was 30,703, of which 1,772 were civil servants and 28,931 were in the private sector. The number of employees increased by 18.9% during the period under review. In particular, the number of employees in the private sector increased by 20.4%, while the number of employees in the public sector decreased by 0.2%.
In 2020, the average monthly salary in the sector was 475,927 AMD [public sector was 200,211 AMD compared to 494,522 AMD in the private sector]. During the study period, the average salary increased by 12.8%; 10.4% in the public sector and 11.9% in the private sector.
In March 2021, the average monthly salary was 528,679 AMD [public sector was 221,442 AMD, compared to 547,498 AMD in the private sector]. The average salary decreased by 1.1% compared to March of the previous year; specifically, the average salary in the public sector increased by 2.3%, and decreased by 1.9% in the private sector.
It should be noted that, compared to other markets in the Armenian economy, the telecommunications and communications market is highly competitive. From the moment the second operator, K-Telecom, started operating in the mobile communication market, the deficit in the market disappeared, and rates started to decrease every month.
At the same time, the entrance of Ucom into the telecommunication and communication market of Armenia also created serious competition, which was due to the fact that the country’s Internet market began to develop rapidly, and the tariffs for Internet services began to decrease. Before Ucom entered the market, ArmenTel, which offers high-speed wired Internet, had no serious competitor. The fact that Ucom provided fixed telecommunication services also contributed to ArmenTel providing these services at lower rates and speeding up the process of digitizing telephone communication.
The example of the telecommunications and communication sector of the Republic of Armenia, shows how competition can ensure low prices and high quality.
New on EVN Report
Translating the 2021 Election Results Into Seats
By Harout Manougian
Nikol Pashinyan renewed his parliamentary majority through Sunday’s June 20 early parliamentary election and will keep his position as Prime Minister of Armenia. Harout Manougian translates the election results into seats.
Current Projects and Plans of Azerbaijan in the Conquered Regions of the Artsakh Republic
By Areg Petrosyan
After its victory in the 2020 Artsakh War, Azerbaijan started massive restoration projects in the seven conquered regions of the Republic of Artsakh. These projects will undoubtedly impact Armenia.
Remedial Secession in the Programs and Statements of the Political Forces Competing in Armenian Elections
By Sossi Tatikyan
After the shocking defeat in the war, the use of the notion of “remedial secession” has not been consistent, neither by the authorities nor by other political forces in Armenia. Sossi Tatikian explains.
A Physicist’s Guide to Science Research in Armenia
By Tatev Mkrtumyan
This article is not about the past, the golden decades when science flourished in Armenia. It’s a guide on what can be accomplished in the present and into the future through the lens of one visionary, Dr. Mushegh Rafayelyan.
The Seat
By Talin Grigorian
In this tiny self-declared and unrecognized Republic where her ancestors once lived, Anahit tries to reassess her existence while she wages a battle for the seat.